 Wiki90
Wiki90
Wiki90: 90s Style Encyclopedia on the Web

|

|

|

|




Hatang Kayi language
In today's article we are going to talk about Hatang Kayi language, a topic that has captured the interest of millions of people around the world. From its origin to its impact on today's society, Hatang Kayi language has been the subject of studies, debates and controversies that have marked its evolution over time. With a history dating back centuries, Hatang Kayi language remains relevant today, influencing our thinking, our culture and our decisions. Through this article, we will explore different aspects of Hatang Kayi language, analyzing its importance and role in the modern world. Join us on this journey of discovery and learning!
| Remontado Dumagat | |
|---|---|
| Sinauna, Remontado Agta | |
| Hatang-Kayi | |
| Native to | Philippines |
| Region | Tanay, Montalban, and Antipolo in Rizal, and General Nakar, Quezon |
Native speakers | 2,500 (2000) |
Austronesian
| |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | agv |
| Glottolog | remo1247 |
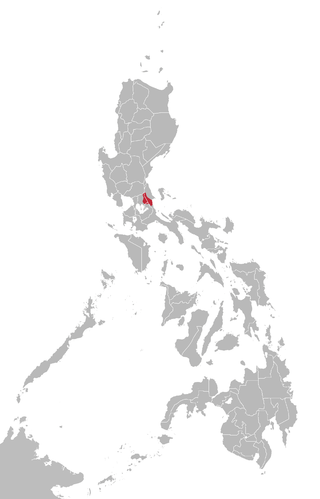 Area where the Sinauna language is spoken | |
Remontado, also known in literature as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and more commonly by the autonym Hatang-Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon (including in Paimahuan, Limoutan), Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages. It is a moribund language.
Terminology
The language is referred to by various terms in linguistic literature. The speakers refer to their language as Hatang-Kayi ('this language') while Remontado is the most common term in English literature used to refer to both the community and their language. Sinauna (meaning 'ancient' or 'old' in Tagalog) is a term used in some literature that originates after the language's discovery in the 1970s but has never been used by the speakers of the language themselves. Remontado Agta has also been used but this is also erroneous as speakers of this language are never referred to as Agta.
Classification
Reid (2010) classifies the language as a Central Luzon language.
Distribution
The Remontado Dumagat were traditionally found in the mountains around the boundary between Sampaloc district in Tanay, Rizal, and General Nakar, Quezon (Lobel 2013:72-73).
Today, Remontado is spoken in the following five villages, where it is only spoken by elderly people over the age of 50 (Lobel & Surbano 2019). Two of the villages are in Barangay Santa Inez, Tanay town, Rizal Province, and three of the villages are in Barangay Limutan, General Nakar town, Quezon Province.
- Minanga (Sentro), Barangay Limutan, General Nakar town, Quezon Province
- Sitio Sari, Barangay Limutan, General Nakar town, Quezon Province
- Sitio Paimuhuan, Barangay Limutan, General Nakar town, Quezon Province
- Sitio Nayon, Barangay Santa Inez, Tanay town, Rizal Province
- Sitio Kinabuan, Barangay Santa Inez, Tanay town, Rizal Province
References
- ^ a b c d Lobel, Jason William; Surbano, Orlando Vertudez (2019). "Notes from the Field: Remontado (Hatang Kayi): A Moribund Language of the Philippines". Language Documentation and Conservation. 13: 1–34. hdl:10125/24796.
- ^ Remontado Dumagat at Ethnologue (18th ed., 2015) (subscription required)
- ^ Reid, Lawrence A. (1994). "Possible Non-Austronesian Lexical Elements in Philippine Negrito Languages". Oceanic Linguistics. 33 (1): 37–72. doi:10.2307/3623000. hdl:10125/32986. JSTOR 3623000.
- ^ https://www.ethnologue.com/language/agv(subscription required)
- ^ Reid, Lawrence A. (2010). "Historical linguistics and Philippine hunter-gatherers" (PDF). In Billings, Loren; Goudswaard, Nelleke (eds.). Piakandatu ami Dr. Howard P. McKaughan. Manila: Linguistic Society of the Philippines and SIL Philippines. pp. 234–260.
- ^ Lobel, Jason William (2013). Philippine and North Bornean Languages: Issues in Description, Subgrouping, and Reconstruction (PhD thesis). University of Hawaii at Manoa. hdl:10125/101972.
 Língua remontado dumagat
Língua remontado dumagat

